| PRODUCT
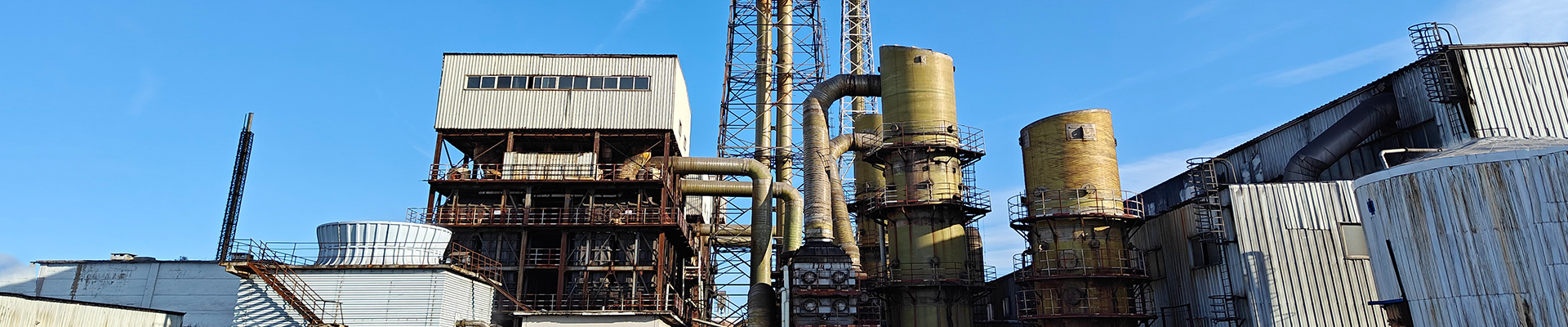
The electric tar catcher adopts three structural forms: concentric circle, tube, and honeycomb. Regardless of the structure, its working principle is to apply high-voltage direct current between the metal wire and the metal tube wall (or electrode plate) to maintain an electric field sufficient to ionize the gas, forming a corona zone between the anode and cathode.
The electric tar catcher adopts three structural forms: concentric circle, tube, and honeycomb. Regardless of the structure, its working principle is to apply high-voltage direct current between the metal wire and the metal tube wall (or electrode plate) to maintain an electric field sufficient to ionize the gas, forming a corona zone between the anode and cathode.
The electric tar catcher adopts three structural forms: concentric circle, tube, and honeycomb. Regardless of the structure, its working principle is to apply high-voltage direct current between the metal wire and the metal tube wall (or electrode plate) to maintain an electric field sufficient to ionize the gas, forming a corona zone between the anode and cathode.
The electric tar catcher adopts three structural forms: concentric circle, tube, and honeycomb. Regardless of the structure, its working principle is to apply high-voltage direct current between the metal wire and the metal tube wall (or electrode plate) to maintain an electric field sufficient to ionize the gas, forming a corona zone between the anode and cathode.